India’s space journey reached a historic milestone with the successful launch of the PSLV-C60, which deployed the Space Docking Experiment (SPADEX) satellites into a 475 km circular orbit. This achievement underscores ISRO’s strides in advanced space technologies, particularly orbital docking, while marking a significant collaboration with private industries and academic institutions.
 Advancing Space Docking Capabilities
Advancing Space Docking Capabilities
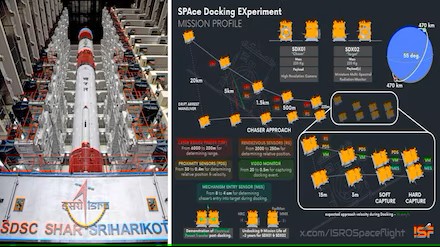
The PSLV-C60 mission carried two identical SPADEX satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target), weighing 220 kg each. These satellites are designed to demonstrate autonomous rendezvous and docking—technologies critical for future manned missions, satellite servicing, and interplanetary exploration. ISRO Chairman S. Somanath lauded the achievement, noting that India now joins the elite group of nations proficient in orbital docking technologies.
“This mission is a key step toward realizing deep space missions, satellite refueling, and the establishment of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS),” Somanath remarked. The SPADEX mission aims to validate operations like spacecraft maintenance and modular assembly in orbit, paving the way for ambitious lunar and Martian missions.
Private Sector’s Integral Role
The mission highlighted the growing role of private players in India’s space sector. Hyderabad-based Ananth Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (ATL) provided critical components for both the SPADEX satellites and the PSLV-C60 rocket. Their contributions included Rendezvous Processing Units (RPUs), DC-DC converters, and 29 key subsystems for the launch vehicle.
Dr. Subba Rao Pavuluri, ATL’s Chairman, emphasized their dedication to supporting ISRO’s missions, stating, “This milestone underscores our commitment to India’s space program. From subsystem manufacturing to satellite integration, ATL is driving innovation in aerospace.”
Empowering Startups and Academia
The mission also showcased innovative collaborations facilitated by IN-SPACe, which enabled the deployment of 10 payloads from startups and research institutions aboard the PSLV’s POEM-4 module. These experiments ranged from green propulsion testing to studying microgravity effects, offering a cost-effective platform for emerging players in space exploration.
Dr. Pawan Goenka, IN-SPACe Chairman, highlighted the initiative’s impact: “By reducing barriers for smaller players, we’re fostering a vibrant ecosystem of innovation in India’s space sector.”
A Vision for the Future
The PSLV-C60 mission signifies a pivotal step toward India’s future space goals, including the establishment of BAS and advanced human spaceflight capabilities. The successful deployment of SPADEX satellites lays the groundwork for sophisticated in-orbit operations, crucial for assembling and maintaining space stations and interplanetary spacecraft.
Through robust public-private partnerships and the integration of innovative platforms like POEM-4, India is solidifying its position as a global leader in space exploration, driving self-reliance and technological excellence.




