RBI Slashes Repo Rate to 5.5%; Shifts to Neutral Stance
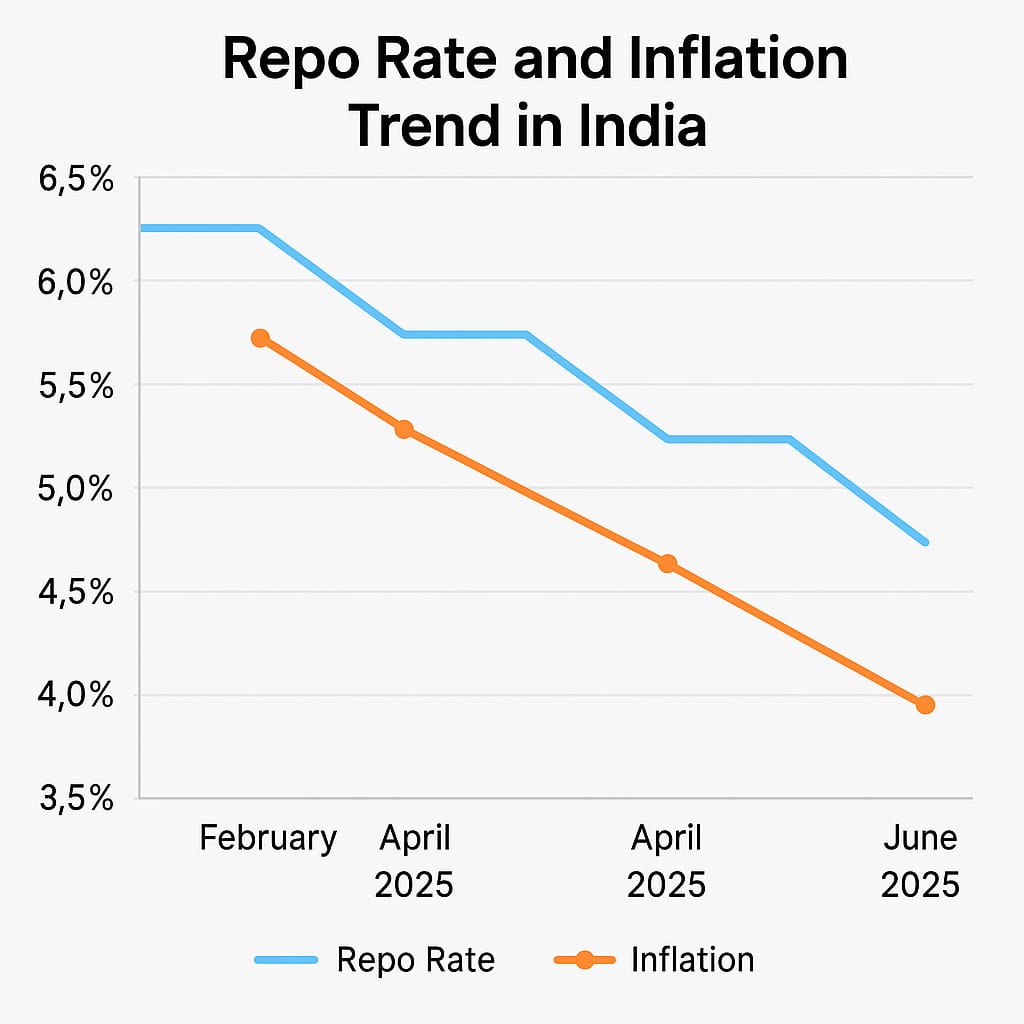
In a significant move to support growth, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on June 6, 2025, cut the repo rate by 50 basis points, bringing it down to 5.5%. This marks the third consecutive rate cut this year. The RBI also changed its monetary stance from ‘accommodative’ to ‘neutral’.
Third Cut This Year
This 50-bps reduction follows earlier cuts of 25 bps each in February and April. With this, the total policy easing so far in 2025 amounts to 100 bps.
RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra cited a detailed review of macroeconomic conditions as the reason behind the decision. The announcement came after the Monetary Policy Committee’s (MPC) three-day meeting, which ended today.
Why the Cut? Falling Inflation
Retail inflation fell to 3.16% in April, down from 3.34% in March, well below the RBI’s 4% comfort level. This consistent decline played a major role in the rate cut.
The RBI also revised its FY26 inflation forecast downward to 3.7%, from the earlier 4%. The quarter-wise inflation outlook now stands at:
-
Q1: 2.9%
-
Q2: 3.4%
-
Q3: 3.5%
-
Q4: 4.4%
Governor Malhotra said this is the lowest inflation India has seen in nearly six years, mainly due to falling food and fuel prices.
Lower EMIs for Borrowers
As repo rates fall, banks reduce their lending rates. This makes home, vehicle, and business loans cheaper, giving relief to both retail and corporate borrowers.
Most banks have already begun adjusting their repo-linked lending rates (EBLR) and MCLR, bringing down EMIs for customers.
CRR Cut to Inject Liquidity
In another bold step, the RBI decided to cut the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by 100 bps, from 4% to 3%. This cut will happen in four phases, each of 25 bps:
-
September 6
-
October 4
-
November 1
-
November 29
This move will inject approximately ₹2.5 lakh crore into the banking system, increasing banks’ ability to lend and lower their funding costs.
No Change in GDP Growth Forecast
Despite global uncertainties, the RBI maintained India’s GDP growth projection at 6.5% for FY26. Quarterly projections are unchanged:
-
Q1: 6.5%
-
Q2: 6.7%
-
Q3: 6.6%
-
Q4: 6.3%
Governor Malhotra expressed confidence in India’s domestic growth, driven by strong services activity and a positive monsoon outlook. However, he warned of risks from geopolitical tensions and trade-related disruptions.
Quick Recap: Previous MPC Meeting
In April 2025, the RBI had reduced the repo rate from 6.25% to 6%. That followed February’s cut from 6.5% to 6.25%. These steps signaled a shift towards pro-growth monetary policy, especially with inflation showing signs of softening.
Key Takeaways
-
Repo Rate now stands at 5.5%
-
Inflation forecast revised to 3.7% for FY26
-
CRR cut by 100 bps, phased from September to November
-
GDP forecast unchanged at 6.5%
-
Banks likely to cut EMIs further
Conclusion:
The RBI’s latest policy moves aim to revive economic momentum without compromising inflation control. With lending likely to grow and consumer loans getting cheaper, the central bank seems ready to support both growth and stability in a cautious but steady manner.
Also Read:
➡️ Govt Steps Up Kharif Fertilizer Supply, Backs Natural Farming




