MSP Coverage Expanded from 10 to 87 Forest Products
MSP Coverage Expanded from 10 to 87 Forest Products
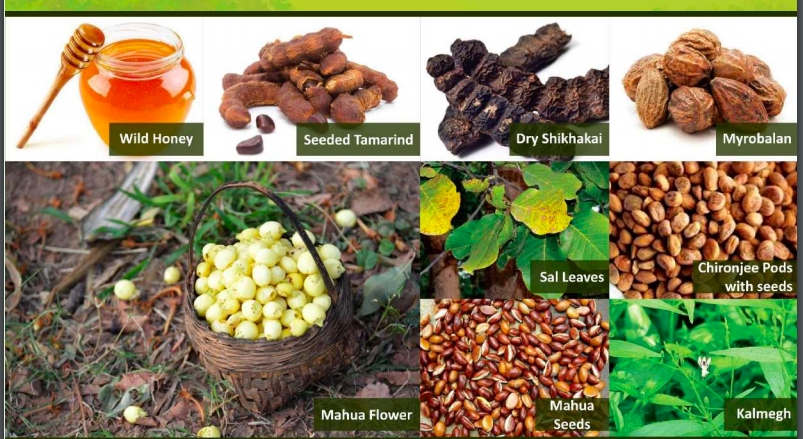
What began with MSP support for just 10 minor forest produce items in 2013–14 has now expanded to 87 notified products. This significant increase reflects the government’s sustained efforts to recognise the economic value of forest-based livelihoods and protect tribal collectors from market exploitation.
Under the PMJVM scheme, MSP ensures fair compensation for activities such as collection, primary processing, storage, and transportation of forest produce. The Ministry has released ₹319.65 crore so far to State Governments as revolving funds for procurement at MSP.
Van Dhan Vikas Kendras Drive Value Addition
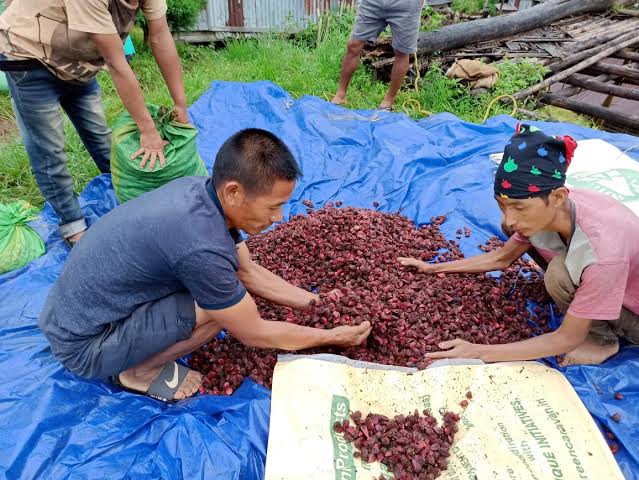
A cornerstone of the PMJVM initiative is the establishment of Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (VDVKs), which function as clusters of tribal Self-Help Groups (SHGs). Each VDVK typically consists of around 15 SHGs and supports up to 300 tribal members, enabling collective processing and marketing.
Since 2019–20, ₹61,212.7 lakh has been sanctioned for setting up 4,125 VDVKs, benefiting over 12.33 lakh tribal members nationwide. These centres play a crucial role in enhancing income through value addition and economies of scale.
Focus on Processing, Branding and Marketing
Value addition activities under the VDVK framework include processing and packaging of products such as Mahua laddus and oil, tamarind cakes and pickles, Harra powder, and a wide range of bamboo-based items including furniture, handicrafts, and utility products.
Finished products are marketed through TRIFED’s “TRIBES India” retail outlets and digital platforms such as tribesindia.com, ONDC, Amazon, and Flipkart, significantly expanding market reach and consumer visibility.
Special Support for Vulnerable Tribal Groups
Under the Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya MahaAbhiyaN (PM JANMAN), additional support has been extended to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs). An amount of ₹2,298.05 lakh has been sanctioned for establishing 539 VDVKs, benefiting nearly 46,000 PVTG members.
These targeted interventions aim to integrate vulnerable tribal populations into mainstream economic activities while preserving traditional knowledge systems.
Strengthening Supply Chain and Capacity Building
To address challenges such as low demand and quality deterioration, State Implementing Agencies are required to dispose of procured MFPs within six months. This reduces storage costs and prevents loss of value.
TRIFED also conducts regular capacity-building programmes for tribal members, covering primary processing, entrepreneurship, branding, and enterprise development to ensure long-term sustainability.
Retail Network and Regional Status
At present, TRIFED operates 116 Tribes India outlets across the country, including five outlets in Kerala located at Ernakulam, Wayanad, Kochi, Cochin, and Thiruvananthapuram. One outlet functions at Ennuru Heritage Village in Wayanad.
The government clarified that no proposal has been received for MSP-based MFP procurement from the Wayanad Lok Sabha constituency, and there is currently no plan to expand the retail outlet network.
Empowering Tribals Through Market Access
The PMJVM framework reflects a shift from welfare to empowerment by linking tribal producers directly with markets. By ensuring price security, encouraging value addition, and strengthening institutional support, the scheme aims to make forest-based livelihoods sustainable and resilient.
These measures underline the government’s broader vision of inclusive growth, economic justice, and self-reliance among India’s tribal communities.